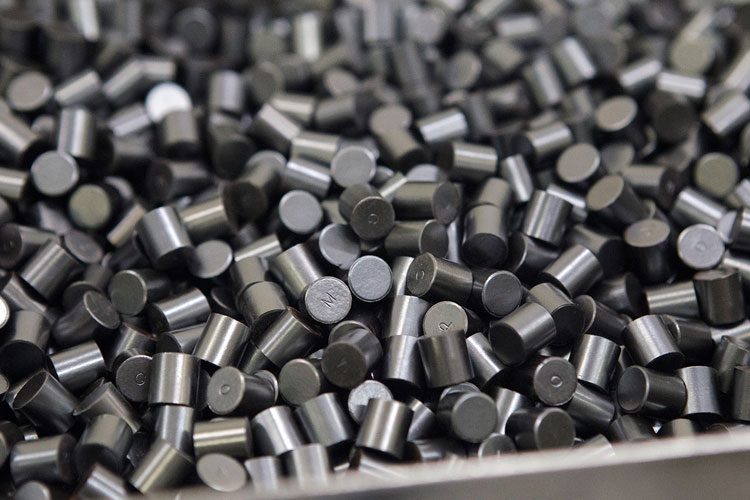
Zirconium is a very strong, malleable, ductile, lustrous silver-gray metal. Its chemical and physical properties are similar to those of titanium. Zirconium is extremely resistant to heat and corrosion. Zirconium is lighter than steel and its hardness is similar to copper. When it is finely divided, the metal can spontaneously ignite in air, especially at high temperatures. Zirconium powder is black and is regarded as very dangerous fire hazard. Zirconium does not dissolve in acids and alkalis.
Zirconium is used in alloys such as zircaloy, which is used in nuclear applications since it does not readily absorb neutrons. Also used in catalytic converters, percussion caps and furnace bricks. Baddeleyite and impure zirconium (zirconia) are used in lab crucibles.
The major end uses of zircon (ZrSiO4) are refractories, ceramic opacification and foundry sands. Zircon is also marketed as a natural gemstone used in jewelry. The metal also has many other uses, among them in photographic flashbulbs and surgical instruments, to make the glass for television, in the removal of residual gases from electronic vacuum tubes, and as a hardening agent in alloys, especially steel. The paper and packaging industries are finding that zirconium compounds make good surface coatings because they have excellent water resistance and strength.
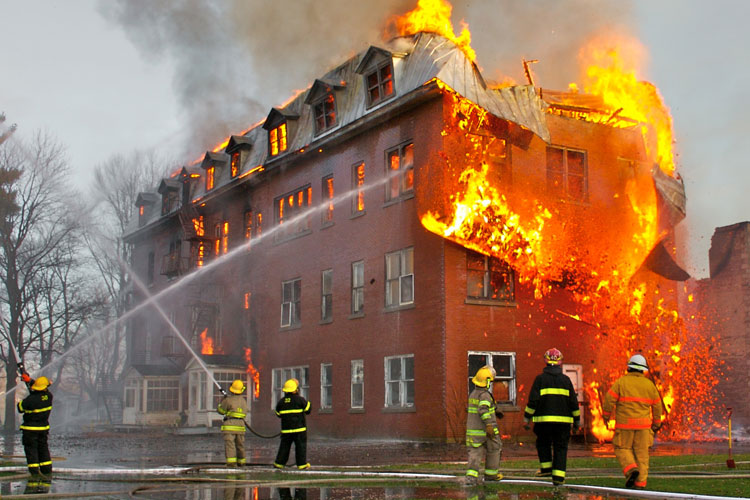
Zirconium Dust is Combustible and is an Explosion Hazard:
When most people think of controlling dust in the workplace, they think of taking steps to avoid inhaling dusts to prevent health problems. However, the accumulation of combustible dusts in the workplace can lead to far greater consequences. As seen in recent years, neglect of housekeeping and improper handling of combustible dusts can lead to property damage, injuries and loss of life.
Zirconium is a very strong, malleable, ductile, lustrous silver-gray metal. Its chemical and physical properties are similar to those of titanium. Zirconium is extremely resistant to heat and corrosion. Zirconium is lighter than steel and its hardness is similar to copper. When it is finely divided, the metal can spontaneously ignite in air, especially at high temperatures. Zirconium powder is black and is regarded as very dangerous fire hazard. Zirconium does not dissolve in acids and alkalis.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) defines a combustible dust as “a combustible particulate solid that presents a fire or deflagration hazard when suspended in air or some other oxidizing medium over a range of concentrations, regardless of particle size or shape.” In general, combustible particulates having an effective diameter of 420 μm or smaller, as determined by passing through a U.S. No. 40 Standard Sieve, are generally considered to be combustible dusts. However, agglomerates of combustible materials that have lengths that are large compared to their diameter (and will not usually pass through a 420 μm sieve) can still pose a deflagration hazard. Therefore, any particle that has a surface area to volume ratio greater than that of a 420 μm diameter sphere should also be considered a combustible dust. The vast majority of natural and synthetic organic materials, as well as some metals, can form combustible dust. The NFPA’s Industrial Fire Hazards Handbook states, “any industrial process that reduces a combustible material and some normally non-combustible materials to a finely divided state presents a potential for a serious fire or explosion.”
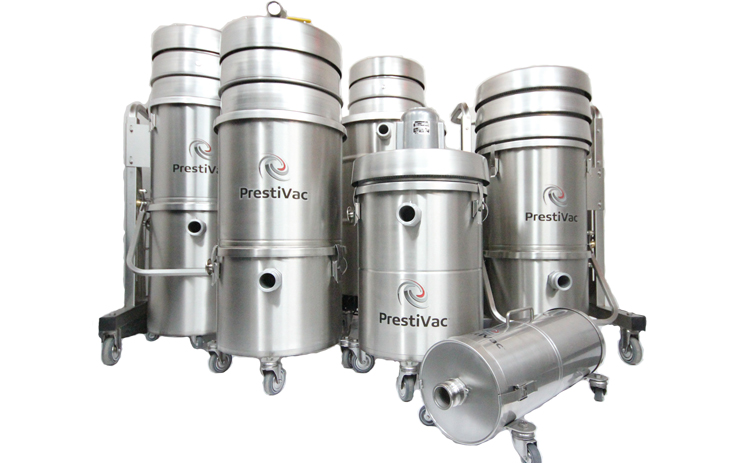
Suggested Industrial Vacuums for Recovery of Toxic & Combustible Dust
PrestiVac HEPAPlus* Vacuums are specifically designed to safely vacuum toxic dusts. Equipped with a Certified Absolute HEPAPlus*filter with an efficiency of 99.995% on 0.2 micron so there is no risk of exposure or contamination for the operator or the environment. These vacuums are tested for absolute filtration. Testing Method: IEST RP-CC034.3. H14. MIL-STD 282 / A.S.T.M. - D2986-91. MPPS method EN 1822.
PrestiVac Explosion Proof/Dust Ignition Protected Vacuums are designed to safely vacuum explosive, flammable, combustible conductive* dusts. Our Explosion Proof/Dust Ignition Protected Vacuums are completely grounded and static dissipating because they are built entirely with non-sparking metals and do not have any painted components so there is no risk of fire or explosion from a spark or static build up. All the electrical components, including the motor and starter are totally enclosed so there is no source of ignition. Our explosion proof vacuum cleaners comply with NFPA 484 guidelines and are an effective tool for good housekeeping practise as per OSHA.
Which Industries are at Risk with Zirconium Dust?