Class/Division of Hazardous Locations
There are products created for specific classes/divisions of work areas. It is, therefore, crucial to have a thorough understanding of the Class/Division system.
Area Classification
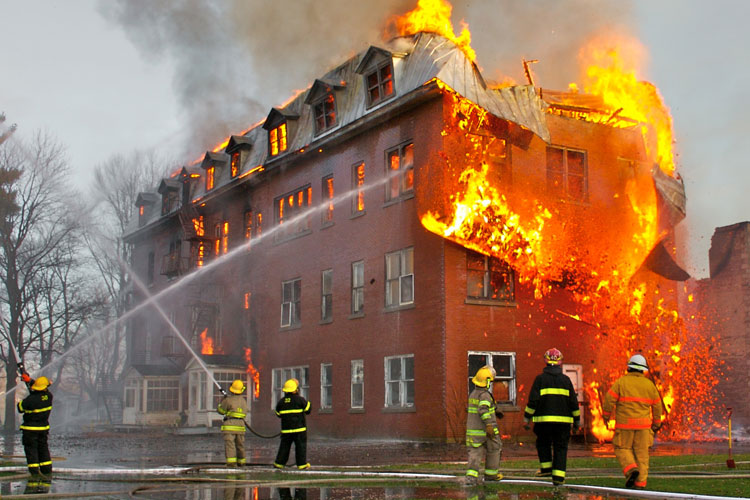
When analysing a facility, each room, section and area should be viewed individually when determining its classification. This classification process provides information on the hazardous materials that may be present and the potential dangers that may occur, as well as the proper equipment and safety procedures to be installed and used in the area.
The NFPA Publication 70 NEC and CEC is the North American classification system that is used extensively. They indicate the types and concentration of hazardous materials that may be present and that may act as an ignition source in a fire or explosion.
The classification of an area is divided into three categories; Class, Division and Group. In order to properly classify an area, one must have a thorough understanding of the space in question.
Class Definition
The first of the three categories used to describe a location is Class. The NFPA Publication 70 NEC and CEC have designated three possible classes; Class I, Class II and Class III, each class outlining a type of hazardous material that may be present.
- Class I locations are those with flammable vapours and gases
- Class II locations are those that may contain combustible dust
- Class III locations are those that are hazardous because of the potential presence of ignitable fibres or flyings
Division Definition
Each Class mentioned is further divided into divisions. The Division defines the likelihood of the hazardous material to be present in a flammable concentration.
Group Definition
Depending on the material involved, its explosive characteristics may vary. Materials have been placed in groups based on their ignition temperatures, safe clearance and maximum explosion pressures. Combustible and flammable gases have been divided into four groups.
Temperature Class Definition
The temperature classes are used to specify the maximum operating temperature of the equipment without exceeding the ignition temperatures of the materials being used. Ignition temperature is the minimal temperature required (at normal atmospheric pressure) in the absence of a spark to kick-start a combustion reaction.
Markings
The rules for marking the electrical equipment are uniformly in the standards relating to general technical requirements. The equipment must be distinctly marked in accordance to the classified area in which it can be installed.
The minimal marking must indicate the following:
- Class
- Division
- Group
- The maximum safe operation temperature
- Any special conditions that have to be observed (such as NEC section 500-5(d))
Execution to NEC/CEC Standards
Hazardous (Classified) Locations in Accordance with Article 500, NEC - 1990